As lithium-ion batteries achieve higher energy densities, battery safety has become a top industry priority. A research team from the Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Lanzhou University and the Guangdong Provincial Laboratory of Advanced Energy Science and Technology, has introduced a next-generation polyimide battery separator designed to withstand extreme temperatures and improve battery reliability.

🔬 Why Battery Separators Matter in Lithium-Ion Safety
Separators are critical components in lithium-ion batteries. They physically isolate the anode and cathode while allowing ions to pass through. However, traditional polyolefin separators have key safety drawbacks:
- Low thermal stability: prone to shrinkage above 120°C
- Irregular pore distribution: increases risk of short circuits
- Weak mechanical integrity under high-stress conditions
With energy densities now reaching up to 300 Wh/kg, these weaknesses pose a serious risk in high-power applications.
🛡️ The Polyimide Advantage: A Safer Separator Material
Polyimide has long been considered ideal for next-generation separators due to:
- Exceptional heat resistance
- High mechanical strength
- Superior chemical stability
The Chinese research team utilized ion track technology, enabled by the Lanzhou Heavy Ion Accelerator, to develop a new fabrication method for producing polyimide separators with uniform pore channels.
🚀 Key Performance Features of the New Polyimide Separator
| Feature | Performance Metric |
| Thermal Stability | No shrinkage at 450°C |
| Mechanical Strength | Up to 150.6 MPa |
| Pore Size Consistency | Standard deviation < 6% |
| Pore Alignment | Vertically aligned, tortuosity = 1 |
These features collectively address the core safety issues that plague commercial lithium-ion batteries.
🔋 Battery Performance Test Results
1. Lithium Symmetric Cell Test
- Current density: 3 mA/cm²
- Cycle performance: Stable operation for 1,200 hours
- Effect: Uniform lithium deposition, suppression of dendrite growth
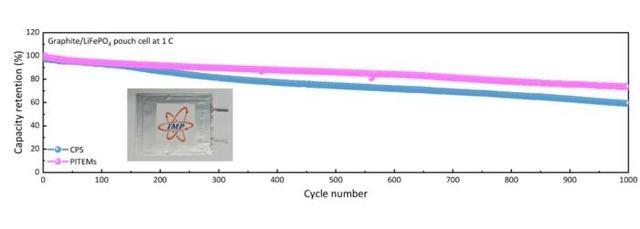
2. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Pouch Cell
- Cycle life: 1,000 cycles at room temperature
- Capacity retention: 73.25%
- High-temp reliability: Operated safely at 150°C
These results indicate the material’s potential for longer lifespan, higher temperature tolerance, and safer energy storage.
🌍 What This Means for the Future of Lithium Battery Technology
This innovation represents a major step toward safer lithium battery systems, especially as demand rises for high-energy EVs, grid-scale storage, and aerospace-grade batteries.
The team’s research, published in ACS Nano, outlines not only a new material but a scalable manufacturing process—opening the door to commercial production of high-performance polyimide separators for mass-market applications.
